研究概要
加齢に伴う骨格筋の萎縮および生活習慣病の発症を予防する機能性食品に関する研究
食酢(醸造酢)に含まれる主要な酸味成分である酢酸は、空腹時には生体のエネルギー源として作用し、摂食時には体脂肪蓄積を抑制する機能を有します。肥満と糖尿病を発症する動物を用いた研究において、酢酸を継続的に摂取することにより、肥満の抑制、耐糖能の改善、さらに骨格筋における脂質代謝が促進されることが明らかになりました。現在は、酢酸が骨格筋においてどのようなメカニズムで脂質代謝を促進するように作用するのか、また酢酸が高齢者の骨格筋萎縮やサルコペニア肥満を予防する可能性についても検討しています。今後は、酢酸の機能性を活かした食品の開発にも繋げていきたいと考えています。
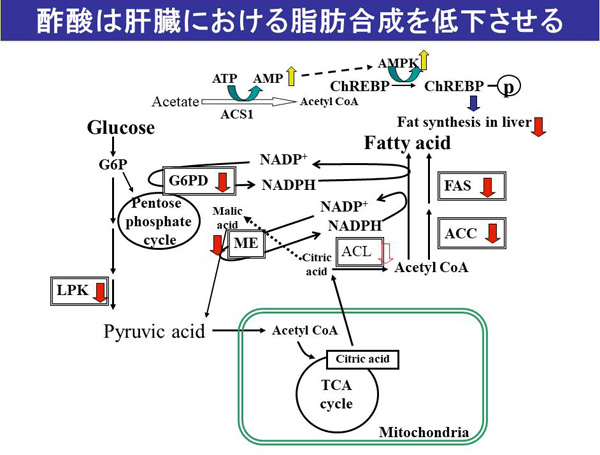
Acetic acid is dominantacid component in vinegar. Previously we found that free acetic acid was formed concomitantly with the production of ketone bodies as a final product of enhanced β-oxidation of fatty acids and utilized as a fuel in extra hepatic tissues under the starving condition. While, when acetic acid was taken daily by obesity-linked type 2 diabetic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats under the fed condition, acetic acid protected OLETF rats against obesity. Acetic acid contributed to protect from the accumulation of lipid in the liver as well as abdominal fat of OLETF rats. It was indicated that exogenously-administered acetic acid would have effects on lipid metabolisms both in liver and skeletal muscles and have function that work against obesity and obesity-linked type 2 diabetes. Now we study on the function of acetic acid to prevent sarcopenic obesity or ageing muscle atrophy.
瀬戸内海で養殖されたマガキの含有成分が季節によりどのように変化するか
瀬戸内海、とりわけ岡山、広島、兵庫の海域は全国でも屈指の牡蠣の養殖場ですが、養殖海域や収穫時期の違いにより牡蠣の栄養成分および呈味成分は異なると考えられています。本研究室では、先ず養殖海域や収穫される時期の違いが牡蠣の成分にどのような影響を与えるか明らかにすることを目的として、牡蠣に豊富に含まれる炭水化物(グリコーゲン)、タンパク質、脂質、タウリン、亜鉛、また旨味成分として、核酸系成分、アミノ酸系成分、有機酸系成分などを解析し、岡山、広島、および兵庫の養殖場で収穫された牡蠣に含まれる成分の季節的な動態を解析しています。また牡蠣に特異的に多く含まれる亜鉛、タウリンの生理機能性、さらに生牡蠣と加熱加工処理を施した牡蠣の成分組成の違いについても解析を行い、牡蠣の栄養的、呈味的な特性を検討しています。


